What is SaaS, and why is it the backbone of modern enterprise software? As cloud computing continues reshaping technology landscapes, software-as-a-service (SaaS) is gaining unmatched prominence. IT managers, cybersecurity experts, and CEOs worldwide face questions about SaaS’s benefits, security implications, and business value.
This guide offers a clear explanation of what SaaS is, how it works, its industry impact, and practical tips for managing SaaS solutions securely and efficiently.
Understanding SaaS: The Basics
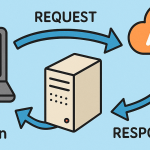
SaaS stands for Software as a Service—a model where software applications are delivered over the internet rather than installed locally on computers. Users access SaaS apps through web browsers, while a provider hosts, maintains, and updates the software on cloud servers.
Key Characteristics of SaaS
Hosted on the Cloud: No need for local installation or hardware resources.
Subscription-Based: Typically paid monthly or annually.
Automatic Updates: Service providers manage updates and patches.
Scalability: Easily scale users and features.
Accessibility: Use anywhere with internet and a web browser.
Popular examples include Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox, and Zoom, showing SaaS’s wide industry adoption.
Why SaaS Matters to IT and Cybersecurity Professionals
SaaS’s cloud-centric architecture transforms traditional IT by reducing infrastructure costs and simplifying software management. However, it also introduces cybersecurity and compliance challenges.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Data Protection: Ensure SaaS vendors comply with encryption, backup, and regulatory mandates.
Access Management: Control user permissions and implement multi-factor authentication.
Vendor Risk: Conduct thorough risk assessments and review SLAs.
Shadow IT: Discover and govern SaaS apps in use without IT knowledge.
For IT managers, SaaS governance involves aligning convenience with security policies.
Benefits of SaaS for Organizations Worldwide
SaaS provides numerous strategic advantages that attract CEOs and founders:
Cost Efficiency: No large upfront licensing costs or maintenance fees.
Rapid Deployment: Instant accessibility enables quick rollouts.
Flexibility: Scale up or down based on demand.
Collaboration: Cloud-native tools improve teamwork regardless of location.
Continuous Innovation: Providers regularly deliver improvements and features.
Industries from healthcare to finance leverage SaaS for agility and digital transformation.
Risks and Challenges of SaaS Adoption
Despite benefits, SaaS adoption presents risks that must be carefully managed:
Data Privacy Vulnerabilities: Entrusting sensitive data to third parties demands strict contracts and audits.
Downtime Risks: Dependence on vendor uptime and internet reliability can affect business continuity.
Integration Complexities: SaaS tools may not easily integrate with legacy systems.
Compliance Risks: Handling data across borders can complicate legal compliance.
Effective risk mitigation requires collaboration among IT, legal, and security teams.
Best Practices for Managing SaaS Security
Implementing these actionable tips helps organizations maximize SaaS benefits while minimizing risks:
Conduct SaaS inventory audits to track usage.
Enforce strong authentication and single sign-on (SSO).
Regularly review vendor security certifications and performance metrics.
Implement data encryption for sensitive information.
Educate employees on safe SaaS use and phishing awareness.
Establish incident response plans involving SaaS providers.
Such governance strengthens security postures and compliance readiness.
SaaS Trends Shaping the Future of IT
As the SaaS market grows, several trends redefine enterprise technology:
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered SaaS automates workflows and insights.
Vertical SaaS: Specialized software tailored to specific industries like law, retail, or healthcare.
API-First SaaS: Easier integration capabilities across varied cloud ecosystems.
Increased Focus on Privacy: Privacy-by-design features embedded in SaaS architectures.
Staying current on these trends helps IT leaders anticipate needs and plan strategically.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on SaaS
1. What is SaaS in simple terms?
SaaS is software delivered online where users access it via the internet without installing it locally.
2. How is SaaS different from traditional software?
Traditional software requires installation on local machines, while SaaS operates on cloud servers with subscription pricing.
3. Is SaaS secure for sensitive data?
SaaS security depends on vendor practices, encryption, user access controls, and compliance audits.
4. Can SaaS integrate with existing systems?
Many SaaS solutions offer API access and connectors, but integration complexity varies.
5. What industries benefit most from SaaS?
Virtually all industries use SaaS, with finance, healthcare, retail, and education among heavy adopters.
Conclusion: Embrace SaaS with Security and Strategy
Understanding what is SaaS is essential for IT managers, cybersecurity professionals, and corporate leaders operating in today’s cloud-first environments. SaaS brings transformative flexibility and cost savings but also demands vigilance in security and governance.
To harness SaaS responsibly, implement robust security controls, conduct comprehensive vendor assessments, and continually train your workforce. This balance of innovation and caution empowers organizations to thrive responsibly.
Embrace SaaS today—equip your teams with the knowledge and tools to leverage cloud software securely and strategically for a competitive edge.