Have you ever wondered how your computer connects to websites, emails, or apps seamlessly? The answer lies in one fundamental element of the internet — the IP address. Every device that connects to the web has one, making it a digital fingerprint that identifies you online. But what is an IP address, and why is it so crucial for businesses, cybersecurity experts, and IT professionals?
In this guide, we’ll break down what an IP address is, how it functions, its types, and most importantly — how to protect it in an increasingly connected world.
What is an IP Address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique numerical label assigned to every device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It serves two main purposes:
Identification – It identifies the host or network interface.
Location Addressing – It provides the location of the device in the network.
In simpler terms, think of an IP address as your home address on the internet. When you send or receive information online, your IP ensures that data reaches the correct destination.
How Does an IP Address Work?
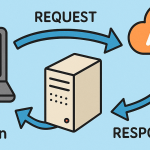
Every time you go online — visiting a website, streaming a video, or sending an email — your device communicates through IP addresses.
Here’s how the process works:
Your device connects to your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
The ISP assigns your device an IP address.
When you access a website, your IP sends a request to the web server.
The server responds, delivering the requested data back to your IP address.
This exchange happens in milliseconds, ensuring smooth communication between devices globally.
Types of IP Addresses
There are different categories and types of IP addresses based on functionality and scope. Understanding these helps IT managers and cybersecurity specialists manage network infrastructure effectively.
1. IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4):
The most common format, consisting of four sets of numbers (e.g.,192.168.1.1).
IPv4 allows around 4.3 billion unique addresses.IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6):
Developed to overcome the shortage of IPv4 addresses. IPv6 uses a 128-bit system (e.g.,2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334) and supports an enormous number of unique addresses.
2. Public vs Private IP Addresses
Public IP Address: Assigned by your ISP and used to communicate over the internet. It’s visible to external networks.
Private IP Address: Used within local networks (like your home or office). Devices in the same network share a private IP to communicate internally.
3. Static vs Dynamic IP Addresses
Static IP Address: Remains fixed and is manually configured. Ideal for servers and businesses that need consistent access.
Dynamic IP Address: Assigned automatically by the network when you connect. It changes periodically and is commonly used for residential connections.
Why IP Addresses Matter in Cybersecurity
For cybersecurity professionals, understanding and monitoring IP addresses is essential for identifying potential threats, attacks, and vulnerabilities.
1. Tracking Malicious Activity
Cybercriminals often use spoofed or masked IP addresses to hide their location. Threat intelligence tools analyze suspicious IPs to detect and block malicious actors.
2. Access Control and Authentication
Organizations use IP-based restrictions to allow only authorized devices to access sensitive systems or networks.
3. Network Forensics
In incident response, analyzing IP logs helps trace cyberattacks back to their source and uncover infiltration routes.
4. Geo-Blocking and Filtering
IP addresses reveal geographical information, enabling companies to block traffic from high-risk regions.
How to Find Your IP Address
Finding your IP address is simple, and the method varies by device:
On Windows:
Open Command Prompt
Type
ipconfigYour IPv4 address will appear under “Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi”
On macOS:
Go to System Preferences → Network
Select your network connection and click Advanced
Find your IP under TCP/IP tab
On Smartphones:
Go to Settings → Wi-Fi → Network details to see your IP address.
How to Protect Your IP Address
Your IP address can reveal your approximate location and online activities, making it a valuable target for cybercriminals. Protecting it is crucial for privacy and security.
1. Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN masks your real IP address, routing your internet traffic through encrypted servers, making it nearly impossible for hackers or websites to track you.
2. Use a Secure Firewall
A firewall monitors incoming and outgoing traffic, blocking suspicious access attempts that may expose your IP.
3. Avoid Clicking Unknown Links
Phishing emails or malicious links can expose your IP to attackers. Always verify the source before engaging.
4. Regularly Update Network Hardware
Ensure your router firmware is up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities that expose IP details.
Common Misconceptions About IP Addresses
| Myth | Reality |
|---|---|
| IP addresses reveal your exact location | They show only an approximate region or ISP |
| Changing your IP guarantees anonymity | Without a VPN, your activity can still be traced |
| All IPs are unique worldwide | Private IPs can repeat across local networks |
The Future of IP Technology
With the growth of IoT (Internet of Things) and 5G networks, the demand for IP addresses continues to rise. IPv6 adoption is crucial for supporting billions of connected devices globally.
Moreover, advanced IP intelligence systems are enhancing network visibility and threat detection for enterprises.
Key Takeaways
An IP address is the digital identifier of every device connected to a network.
There are two main versions: IPv4 and IPv6.
IPs can be public/private or static/dynamic, each with distinct uses.
Protecting your IP helps prevent cyber threats, data breaches, and identity tracking.
Using tools like VPNs, firewalls, and network monitoring is essential for security.
FAQs About IP Addresses
1. What is the main purpose of an IP address?
An IP address identifies devices on a network and enables data communication between them.
2. Can someone hack me through my IP address?
While it’s difficult, it’s possible if your system has vulnerabilities. Using a VPN and firewalls reduces this risk.
3. Is my IP address the same everywhere I go?
No. Your IP changes depending on your network and internet connection.
4. What’s the difference between IPv4 and IPv6?
IPv4 uses 32-bit numeric addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit, providing exponentially more unique addresses.
5. Can I hide my IP address completely?
You can mask it using VPNs or proxies, but total anonymity online is nearly impossible.
Conclusion
Understanding what an IP address is helps you navigate the digital world safely and efficiently. Whether you’re an IT manager, cybersecurity expert, or entrepreneur, protecting your network identity is vital. By securing your IP and monitoring network traffic, you strengthen your defense against online threats.
Stay secure. Stay informed. Protect your IP.