Have you ever wondered what are APIs and why they’ve become essential in today’s digital ecosystem? Whether you’re an IT manager, cybersecurity specialist, or a business leader, APIs are the invisible bridges that connect applications, exchange data, and enable automation.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the backbone of modern digital transformation. They let systems “talk” to each other securely and efficiently — whether you’re connecting a payment gateway to your website or integrating security tools in your tech stack.
But while APIs power business innovation, they also introduce new security challenges. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down what are APIs, their types, benefits, working mechanism, security best practices, and their importance to IT and cybersecurity leaders worldwide.
What Are APIs and Why They Matter
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a structured set of protocols and definitions that allow two software applications to communicate with each other. In simple terms, an API acts as a messenger that takes a request, tells a system what to do, and then returns the result.
For example:
When you use a weather app, the app connects to an API that fetches real-time weather data.
When you pay online, an API connects your bank to the merchant’s website securely.
Why APIs Matter for Business and Security
Integration: APIs make it easier for systems to share data and work together.
Scalability: They allow organizations to scale services without rebuilding entire systems.
Innovation: APIs enable faster product development and integration with third-party apps.
Security Awareness: Since APIs connect critical systems, securing them is vital to prevent data leaks and breaches.
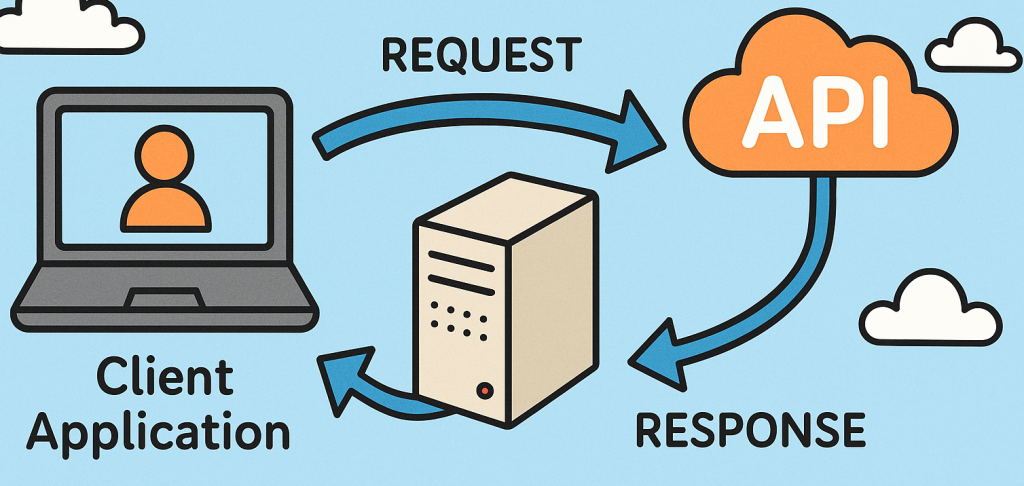
How APIs Work: The Behind-the-Scenes Process
Understanding how APIs function helps IT managers design more efficient and secure systems.
Here’s how it works in four steps:
Request: A client application sends an API request to a server endpoint (e.g., GET /users).
Processing: The API receives the request, verifies it, and processes it through backend logic.
Response: The server sends back a structured response, often in JSON or XML format.
Integration: The client application displays or uses the data within its own interface.
APIs follow specific architectural styles — the most common being REST, SOAP, and GraphQL.
REST APIs use standard HTTP methods and are lightweight and scalable.
SOAP APIs use XML for communication and are preferred for enterprise-grade transactions.
GraphQL APIs allow clients to request exactly what they need, reducing data transfer.
Types of APIs and Their Business Uses
There isn’t just one kind of API — and knowing the difference helps align your API strategy with business needs.
1. Public (Open) APIs
Accessible to external developers or partners. Examples include Google Maps API or Twitter API.
Use Case: Expanding ecosystem and innovation through open collaboration.
2. Private (Internal) APIs
Used within an organization to connect internal systems or services.
Use Case: Improving operational efficiency and integration between departments.
3. Partner APIs
Shared only with strategic business partners.
Use Case: Secure data exchange and joint ventures, like logistics or payment providers.
4. Composite APIs
Combine multiple data sources or services into one unified interface.
Use Case: Simplifying complex workflows like travel booking or supply-chain dashboards.
CEOs and IT leaders should classify their APIs by visibility — public, private, or partner — to manage both innovation and security risk effectively.
Real-World Examples of APIs in Action
APIs are everywhere — powering nearly every digital service you use daily.
E-Commerce: Payment gateways like PayPal and Stripe use APIs to process secure transactions.
Social Media: Facebook, LinkedIn, and Instagram APIs allow cross-platform content sharing.
Cybersecurity: Threat-intelligence APIs feed real-time attack data into SIEM systems.
Cloud Computing: APIs connect different cloud services for data synchronization and backup.
Healthcare: APIs enable secure data exchange between hospitals, labs, and insurers.
For IT and cybersecurity professionals, APIs are not just technical assets — they’re strategic enablers of agility, automation, and data intelligence.
Benefits of APIs for Organizations
APIs offer tangible advantages for every organization, regardless of size or industry:
Enhanced Productivity: Reuse existing functionalities rather than reinventing them.
Faster Time to Market: Developers can integrate third-party services instantly.
Improved Customer Experience: Seamless integrations deliver better digital experiences.
Data-Driven Decision Making: APIs enable real-time access to business insights.
Stronger Ecosystem Collaboration: APIs foster partnerships and digital ecosystems.
For cybersecurity teams, APIs provide access to threat feeds, vulnerability databases, and security orchestration tools that enhance response times.
API Security: Challenges and Best Practices
APIs introduce flexibility — but also risk. According to Gartner, API attacks are one of the fastest-growing threat vectors in cybersecurity.
Common API Security Risks
Weak authentication or lack of authorization controls.
Exposed endpoints revealing sensitive data.
Lack of encryption during data transmission.
Insecure third-party integrations or dependencies.
Insufficient monitoring and logging of API activity.
API Security Best Practices for IT and Cyber Leaders
Implement Strong Authentication: Use OAuth 2.0 or JWT for secure access control.
Encrypt All Traffic: Enforce HTTPS and TLS protocols for all API communications.
Adopt Least Privilege Principles: Limit each API’s permissions to only what’s necessary.
Use an API Gateway: Centralize monitoring, throttling, and access management.
Enable Rate Limiting: Prevent abuse or DDoS attacks by limiting request rates.
Log and Monitor Everything: Capture access logs for anomaly detection and audits.
Version and Test APIs Regularly: Maintain backward compatibility and security updates.
Conduct Regular Security Audits: Test APIs for vulnerabilities like injection or exposure.
API Governance and Compliance
With APIs becoming business-critical, governance ensures consistency, compliance, and accountability.
Key Governance Areas:
Documentation: Maintain clear technical documentation for every API.
Lifecycle Management: Define creation, versioning, and deprecation policies.
Compliance: Ensure APIs meet GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO security requirements.
Access Control: Manage who can publish, modify, or consume APIs.
Incident Response: Define clear escalation paths for API-related breaches.
When governance and security align, APIs evolve from being potential liabilities to trusted assets.
API Strategy: A Checklist for Leaders
Here’s a practical checklist to help your team manage APIs effectively:
✅ Map all existing APIs (public, private, partner).
✅ Classify APIs by sensitivity and risk exposure.
✅ Apply authentication and encryption policies.
✅ Set rate limits and API gateway rules.
✅ Track performance metrics (latency, error rates, uptime).
✅ Conduct quarterly API vulnerability assessments.
✅ Define KPIs for API adoption and usage.
✅ Educate staff on secure API development and usage.
A well-governed API ecosystem accelerates business innovation while maintaining security and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are APIs in simple terms?
APIs are digital connectors that allow two applications to exchange data or functions securely.
2. What is the main purpose of an API?
The main goal of an API is to simplify integration, automate workflows, and allow secure data sharing between systems.
3. What are the 3 main types of APIs?
Public, Private, and Partner APIs — each serves different audiences and business goals.
4. Why is API security important?
Because APIs often handle sensitive data, insecure APIs can lead to major breaches, data leaks, and compliance violations.
5. How can companies manage APIs effectively?
By implementing API gateways, strong authentication, logging, rate limiting, and continuous security testing.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In today’s hyper-connected world, APIs aren’t just technical tools — they’re strategic business enablers. They empower organizations to innovate faster, integrate smarter, and operate securely.
For IT and cybersecurity professionals, understanding what are APIs means understanding the backbone of digital transformation — and how to protect it.
👉 Call to Action:
Evaluate your current API infrastructure today.
Ask yourself — Are our APIs secure, scalable, and aligned with business goals?
If not, it’s time to strengthen your API strategy to drive innovation — without compromising security.